Lowering Global Warming Potential in XPS Foam Board Production
Over the years, the use of sustainable materials in construction has become increasingly important. Strict environmental regulations and public opinion regarding climate change and pollution has demanded a more environmentally friendly approach from every industry. This includes the production of thermal insulation materials like extruded polystyrene XPS foam boards.
Using XPS foam boards to insulate a building offers multiple environmental benefits in itself as it helps to drastically lower energy usage while being highly durable, water resistant and long lasting. XPS foam is a rigid board insulation produced by a continuous extrusion process. This manufacturing process involves the use of a gas blowing agent. Under F-GAS regulations, manufacturers of XPS foam are required to adopt gas blowing agents with low Global Warming Potential (GWP) and zero effect on ozone depletion.
The Move Away From HFCs
A variety of climate-friendly blowing agents have been or are being developed for use in building/construction foam applications to replace widely used chemicals like CFCs, HCFCs, and HFCs. Freons or hydrofluorocarbons (HFC) are one of the most widespread refrigerant gases on the market and were commonly used in construction.
These gases replaced chlorofluorocarbons (CFC) and hydrochlorofluorocarbons (HCFC), both of which damage the ozone layer. However, HFCs still have a high global warming potential and are being phased out as cost-effective low-GWP alternatives become available. For production of XPS foam boards, low-GWP hydrocarbon (HC) alternatives already comprise more than half of the global market, while CO2 and newer chemicals like HFO-1234ze are also being used.
Different Blowing Agents Compared
XPS foam boards historically used CFC-12 as the blowing agent, before transitioning to HCFC-142b/22 blends. In developed countries like Australia, HFC-134a and HFC-152a then replaced some ozone-depleting substances (ODS) use, but other low-GWP options isobutane, di-methylether, blends of those two agents, and CO2 were also used. HFO-1234ze is the latest innovation in sustainable XPS production and offers superior eco-friendly properties, as seen in the comparison table below.
| Chemical | GWP | ODP (ozone depletion potential) |
| CFC-12 | 10900 | 1 |
| CFC-11 | 4750 | 1 |
| HFC-227ea | 3220 | 0 |
| HCFC-142b | 2310 | 0.065 |
| HCFC-22 | 1810 | 0.055 |
| HFC-134a | 1430 | 0 |
| HFC-245fa | 1030 | 0 |
| HFC-365mfc | 794 | 0 |
| HCFC-141b | 725 | 0.11 |
| HFC-152a | 124 | 0 |
| Cyclopentane | <25 | 0 |
| n-Pentane | <25 | 0 |
| Methyl Formate | <25 | 0 |
| Methylal | <25 | 0 |
| Other HFOs | <25 | 0 |
| Isobutane | 3 | 0 |
| HFO-1234ze | 1 | 0 |
| Di-methyl Ether | 1 | 0 |
| CO2 | 1 | 0 |
Source: epa.gov
Challenges Finding the Ideal Eco-Friendly Blowing Agent
The challenge for XPS foam insulation manufacturers has been to source a blowing agent that offers low GWP and zero effect on ozone depletion while also maintaining thermal conductivity. In the case of JACKON Insulation, this involved assessing the performance of Solstice® GBA (HFO–1234ze) in comparison to CO2 and HFC-152a blowing agents.
JACKON Insulation has manufactured high quality insulation materials and construction boards using XPS foam for more than 25 years and is seen as the innovative industry leader. The company originally produced XPS foam boards using CO2 or HFC-152a blowing agents. However, neither gas stays in the foam, negatively impacting its thermal properties.
The key was to find a gas blowing agent that would help improve on Lambda levels of 34-37 mW/mK using CO2 (JACKODUR® KF) or HFC-152a (JACKODUR® CFR). XPS foam produced using HFC-134a exhibited better thermal conductivity (29-31 mW/mK) but unfortunately at a high global warming potential (GWP) of 1,300*1.
HFO-1234ze Supports Sustainable and High Performance XPS
Working with Honeywell, JACKON Insulation began testing the performance of HFO-1234ze on its XPS foam production line. The focus was on using a low GWP blowing agent that would deliver insulation performance comparable to or even superior in thermal insulating qualities as XPS foam produced with HFC 134a.
Using HFO-1234ze as a blowing agent, JACKON Insulation achieved an XPS foam product with improved thermal conductivity, performing even better than when using HFC-134a. This has allowed the company to produce its range of JACKODUR® Plus boards with Lambda 27 mW/mK for building insulation and 25 mW/mK for the fabrication market while maintaining a GWP of less than 1.
Benefits of XPS Foam Construction Boards
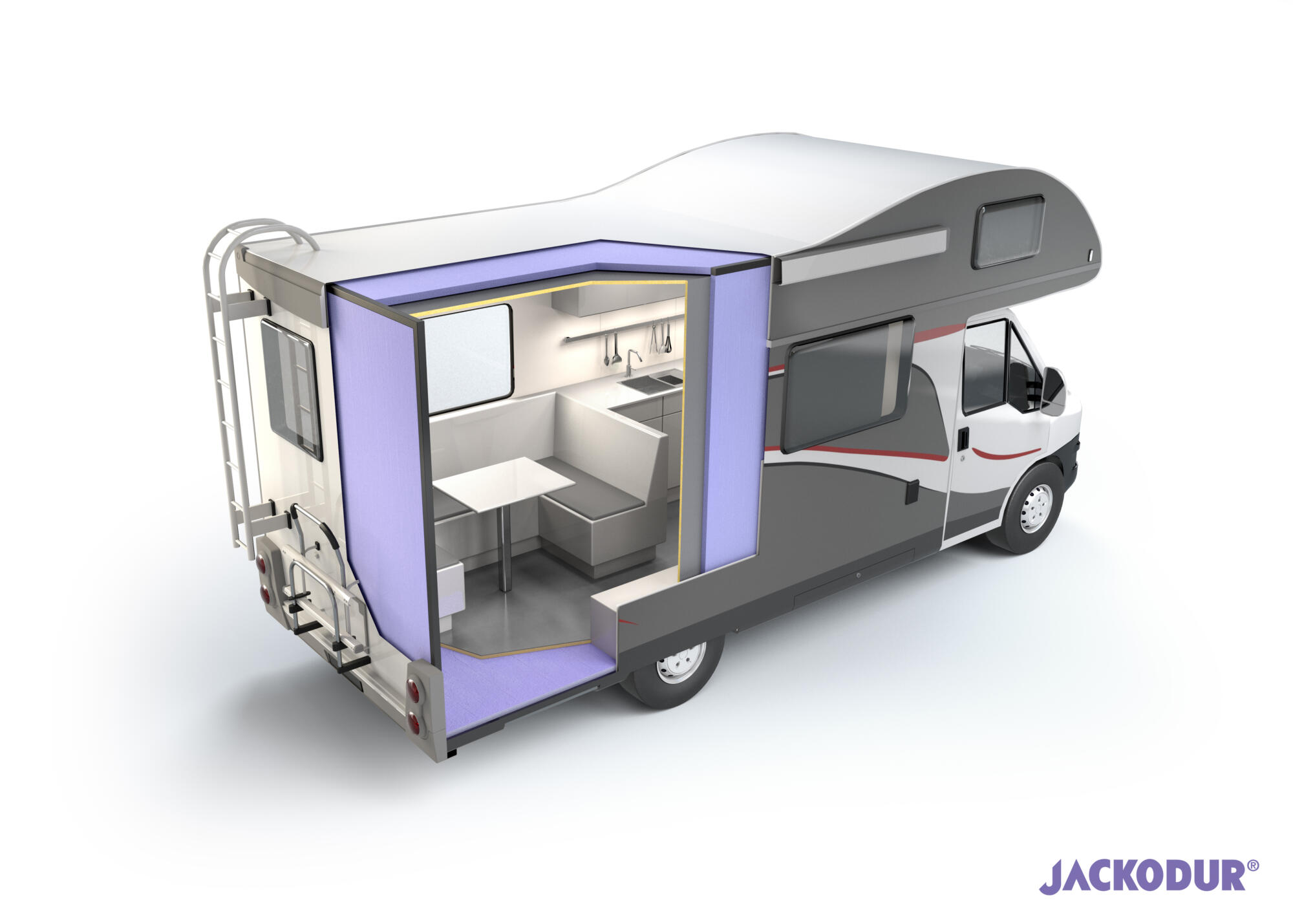
JACKODUR® XPS foam insulation products are ideal for construction/fabrication applications where thermal conductivity is essential, such as refrigerated commercial vehicles, cold rooms, exterior insulation finishing systems and inverted roofs. Other qualities include:
- High compressive strength
- Rot-proof and able to resist moisture
- Lightweight
- Can be trimmed to any shape with a saw, hot wire or cutter
- Long-term durability
- Great long-term R-value
XPS foam insulation is also 100% recyclable and easy to work with. It’s the ideal building solution when you need insulating boards that are resistant to temperature extremes and won’t swell, shrink or absorb moisture.
JACKODUR® XPS Foam Construction Boards Supplied by Liner
For over 35 years, JACKON INSULATION has consistently manufactured high quality insulated products. With a strong focus on the customer, JACKODUR® products can reliably meet the unique needs of both Construction companies and Industrial manufacturers.
At Liner, we’re dedicated to supplying the Construction and Industrial sectors with the highest quality materials from leading brands like JACKODUR®. Contact us today for a quote, product sample, consultation or for more information about JACKODUR® XPS products.
Related Questions
What are HFO refrigerants?
Like HFCs, HFOs contain hydrogen, fluorine and carbon, but they are distinctly different. They are olefins, which mean they have very short atmospheric lifetimes of a few days, leading to environmental benefits.
What is HFO-1234ze exactly?
HFO-1234ze is a hydrofluoroolefin developed as a fourth generation refrigerant to replace fluids as R-134a and as a blowing agent for foam and aerosol applications. HFO-1234ze has zero ozone-depletion potential (ODP=0), a very low global-warming potential (GWP < 1 ), even lower than CO2, and is classified by ANSI/ASHRAE[4] as class A2L refrigerant (lower flammability and lower toxicity).
Are CFCs still used today?
Production of CFCs ceased in 1995. HCFC production will cease in 2020 (HCFC-22) or 2030 (HCFC-123). This means any equipment that uses these refrigerants may operate for 20 or 30 years but new or recycled refrigerant to service it may not be available.